Vaquita The World’s Most Endangered Porpoise, welcome to our exploration of the Vaquita, the world’s smallest and most endangered porpoise species. In this article, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of the Vaquita, exploring its habitat, characteristics, threats, conservation efforts, and the challenges it faces for survival.
Table of Contents
What is a Vaquita?
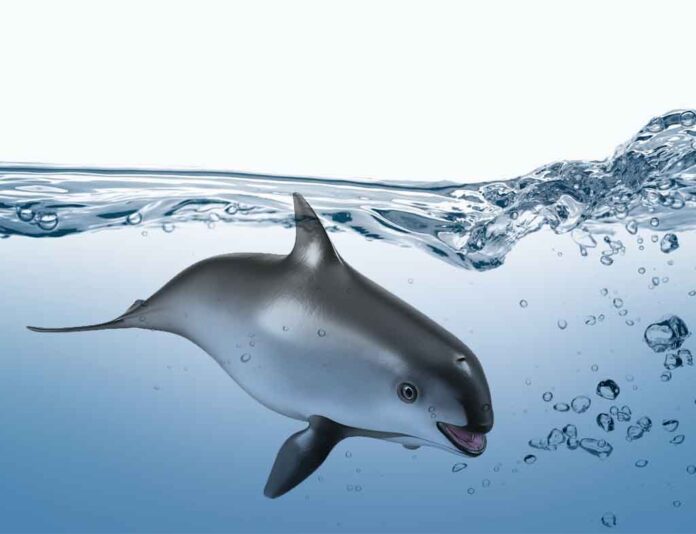
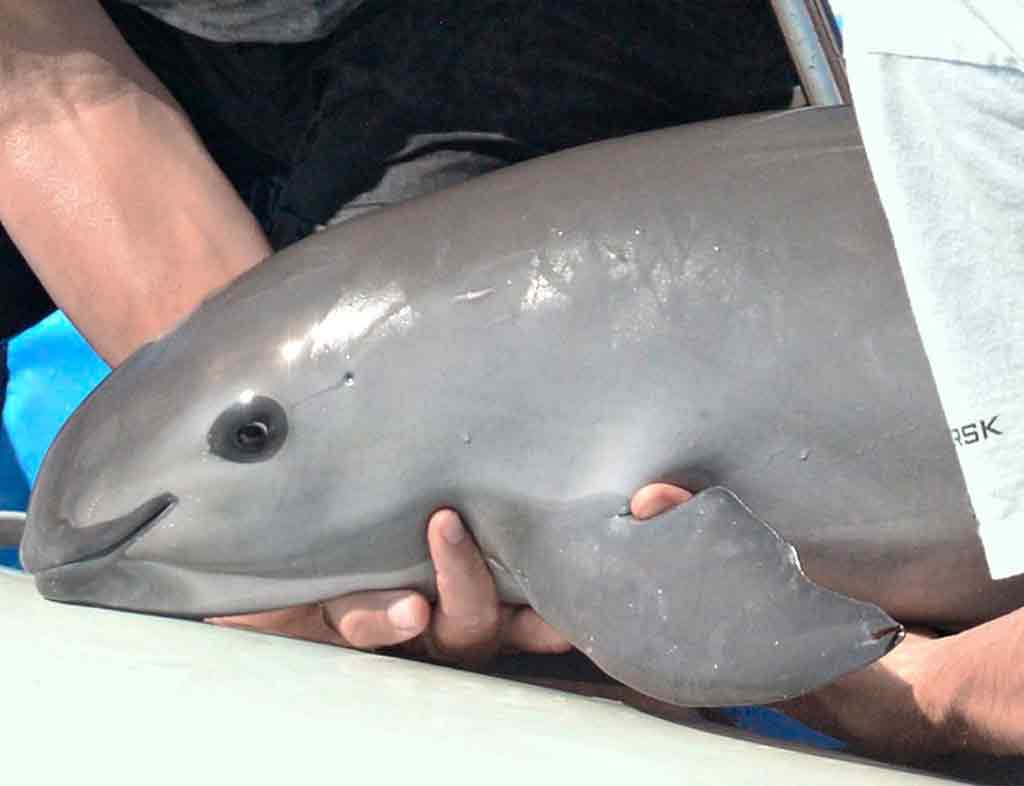
Vaquita The World’s Most Endangered Porpoise, scientifically known as Phocoena sinus, is a rare species of porpoise found exclusively in the northern part of the Gulf of California, Mexico. With a population estimated to be less than 10 individuals, the Vaquita is on the brink of extinction, making it one of the most critically endangered marine mammals on the planet.
Habitat and Range
Vaquitas inhabit the shallow, murky waters of the northern Gulf of California, where they feed primarily on small fish, squid, and crustaceans. Their limited range and specific habitat requirements make them particularly vulnerable to human activities and environmental changes.
Physical Characteristics
Vaquitas are small porpoises, measuring only around 1.5 meters in length and weighing up to 55 kilograms. They have a distinctive dark ring around their eyes and dark patches on their lips and chin, giving them a unique appearance. Their sleek bodies are perfectly adapted for life in the water, with streamlined shapes and powerful flippers for swimming.
Threats to Vaquita
The primary threat to Vaquita The World’s Most Endangered Porpoise is bycatch in illegal fishing operations, particularly the use of gillnets to catch another endangered species, the totoaba fish. Totoaba swim bladders are highly prized in traditional Chinese medicine, leading to a lucrative black market trade that puts Vaquitas at risk of entanglement and drowning in fishing nets.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts to save the Vaquita have been underway for years, with various organizations and governments working together to address the threats facing this critically endangered species. These efforts include monitoring and enforcement of fishing regulations, research and population surveys, and initiatives to promote sustainable fishing practices.
Illegal Fishing and Poaching
Despite conservation efforts, illegal fishing and poaching continue to pose significant challenges to Vaquita conservation. The demand for totoaba swim bladders drives illegal fishing activities in the Gulf of California, leading to an increased bycatch of Vaquitas in gillnets.
Impact of Gillnets
Gillnets are particularly harmful to Vaquitas, as they are designed to entangle fish by their gills, but often unintentionally trap and drown marine mammals, including Vaquitas. Efforts to ban the use of gillnets in the Vaquita habitat have been met with resistance from illegal fishing operations, exacerbating the threat to the species.
Collaborative Conservation Initiatives
International collaboration is essential for the conservation of Vaquitas, as their habitat spans multiple countries and jurisdictions. Collaborative efforts between Mexico, the United States, and international conservation organizations have resulted in joint patrols, surveillance, and enforcement actions to protect Vaquitas and combat illegal fishing.
International Support and Funding
International support and funding are crucial for sustaining conservation efforts and ensuring the survival of the Vaquita. Donor countries, non-governmental organizations, and international conservation funds provide financial assistance for research, enforcement, and community outreach programs in the Gulf of California.
The Role of Local Communities
Local communities living around the Gulf of California play a vital role in Vaquita conservation efforts. Through education, outreach, and alternative livelihood programs, communities are empowered to participate in sustainable fishing practices and support Vaquita conservation initiatives.
Successes and Challenges
While there have been some successes in Vaquita conservation, such as the removal of gillnets from their habitat and increased enforcement efforts, significant challenges remain. Illegal fishing continues to threaten the survival of Vaquitas, requiring ongoing commitment and collaboration from all stakeholders.
Future Prospects of Vaquita The World’s Most Endangered Porpoise
The future of the Vaquita remains uncertain, but with continued conservation efforts and international cooperation, there is hope for their survival. By addressing the root causes of their decline, protecting their habitat, and combating illegal fishing, we can ensure a brighter future for this critically endangered species.
Discovering the Heard Natural Science Museum & Wildlife Sanctuary
Vaquita The World’s Most Endangered Porpoise

1. Why are Vaquitas endangered?
Vaquitas are endangered primarily due to bycatch in illegal fishing operations targeting the totoaba fish.
2. What is being done to save the Vaquita?
Conservation efforts include monitoring and enforcement of fishing regulations, research and population surveys, and initiatives to promote sustainable fishing practices.
3. How many Vaquitas are left in the wild?
The current population of Vaquitas is estimated to be less than 10 individuals, making them one of the most critically endangered marine mammals.
4. What is the main threat to Vaquitas?
The main threat to Vaquitas is bycatch in gillnets used in illegal fishing operations targeting the totoaba fish.
5. How can individuals help save the Vaquita?
Individuals can help save the Vaquita by supporting conservation organizations, raising awareness about the plight of the species, and advocating for sustainable fishing practices in the Gulf of California.












